Peirce Abduction Marbles Logic


Introduction to Peirce Abduction and Its Application in Logic
The concept of abduction, introduced by Charles Sanders Peirce, is a fundamental aspect of logic and reasoning. Abduction is often referred to as the process of forming an explanatory hypothesis, which is a crucial step in scientific inquiry and problem-solving. In this context, the term “Peirce Abduction Marbles Logic” can be seen as a metaphor for understanding the intricate and complex nature of abductive reasoning. Just as marbles can be used to demonstrate simple principles of physics, such as gravity and motion, Peirce’s abduction can be thought of as a tool for navigating the complex landscape of logical reasoning.
Understanding Abduction
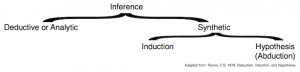
Abduction is distinct from deduction and induction, which are also essential components of the reasoning process. Deduction involves drawing a specific conclusion from a general premise, whereas induction involves making a general conclusion based on specific instances. Abduction, on the other hand, is the process of generating a hypothesis that explains a set of observations or phenomena. This hypothesis is not necessarily proven but is rather a plausible explanation that can be tested further. The application of abduction in logic is vast, ranging from scientific research to everyday problem-solving.
Key Elements of Abductive Reasoning
Abductive reasoning involves several key elements: * Surprise or Anomaly: The process often begins with an observation that does not fit into our current understanding or expectations. * Hypothesis Formation: Based on the anomaly, a hypothesis is formed to explain the observed phenomenon. * Plausibility: The hypothesis must be plausible, meaning it should have some basis in existing knowledge or observation. * Testability: A good abductive hypothesis should be testable, allowing for further investigation to either support or refute it. These elements highlight the dynamic and iterative nature of abductive reasoning, where hypotheses are continuously refined or replaced based on new evidence or observations.
Application of Abduction in Logic
The application of abduction in logic is multifaceted. It is particularly useful in situations where there is incomplete information or when dealing with complex systems. Abduction allows for the generation of hypotheses that can guide further investigation, even in the absence of complete data. This is especially valuable in fields like medicine, where diagnosis often involves abductive reasoning to identify the underlying cause of symptoms. In computer science, abduction is used in artificial intelligence and machine learning to develop models that can explain and predict complex behaviors.
Examples and Illustrations
To illustrate the concept of abduction more clearly, consider a simple example: - Observation: A car does not start. - Hypothesis Formation: Possible explanations could include a dead battery, empty gas tank, or faulty ignition system. - Plausibility and Testability: Each hypothesis is then evaluated for plausibility and testability. For instance, checking the battery or gas level is straightforward and can quickly confirm or rule out these hypotheses.
Challenges and Limitations
While abduction is a powerful tool in logical reasoning, it also comes with challenges and limitations. One of the main issues is the potential for ad hoc hypotheses, which are explanations designed to account for a particular observation but lack broader explanatory power or testability. Additionally, abduction relies heavily on the creativity and knowledge of the individual forming the hypotheses, which can introduce biases and limitations.📝 Note: The effectiveness of abductive reasoning can be significantly enhanced by collaborative efforts, where diverse perspectives and expertise can lead to more robust and well-rounded hypotheses.

Future Directions and Implications
The study and application of Peirce’s abduction continue to evolve, with significant implications for various fields. In an era where data is abundant but often incomplete or noisy, the ability to form plausible hypotheses is crucial. Advances in artificial intelligence and machine learning are also expected to enhance abductive capabilities, allowing for more efficient and accurate hypothesis generation and testing.
Marbles Logic as a Teaching Tool
Using marbles or similar objects can be an engaging way to teach logical concepts, including abduction. By setting up scenarios where marbles follow certain rules or paths, students can be encouraged to use abductive reasoning to explain observed patterns or behaviors. This hands-on approach can make complex logical concepts more accessible and fun, promoting a deeper understanding of the underlying principles.
| Concept | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Deduction | Specific conclusion from a general premise | All humans are mortal. Socrates is human. Therefore, Socrates is mortal. |
| Induction | General conclusion from specific instances | Observing many swans, all of which are white, leading to the conclusion that all swans are white. |
| Abduction | Forming a hypothesis to explain observations | Noticing a car doesn't start and hypothesizing it could be due to a dead battery. |
In summary, Peirce’s abduction is a vital component of logical reasoning, allowing for the formation of explanatory hypotheses in the face of incomplete information. By understanding and applying abductive reasoning, individuals can enhance their problem-solving capabilities and contribute to advancements in various fields. The use of marbles or similar analogies can serve as an innovative teaching method, making complex logical concepts more engaging and accessible. As we continue to navigate the complexities of the world around us, the importance of abduction in logic will only continue to grow, providing a foundation for innovative thinking and discovery.

What is the primary difference between abduction and other forms of reasoning like deduction and induction?
+
Abduction is primarily concerned with forming hypotheses to explain observations, whereas deduction involves drawing specific conclusions from general premises, and induction involves making general conclusions from specific instances.
How does Peirce’s concept of abduction contribute to scientific inquiry and problem-solving?
+
Abduction plays a crucial role in generating hypotheses that can explain observed phenomena, guiding further investigation, and ultimately leading to new discoveries and a deeper understanding of the world.

Can abduction be applied in everyday life, or is it limited to scientific and academic contexts?
+
Abduction is not limited to scientific or academic contexts; it is a fundamental aspect of human reasoning that can be applied in everyday life to solve problems, understand complex situations, and make informed decisions.



